Kann die Dialyse die körperliche Betätigung beeinflussen?

Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), especially those on long-term dialysis show low levels of physical fitness and an increased cardiovascular risk. Systematic exercise increases life expectancy, but also quality of the life in patients with CKD.
What are the health benefits of exercise?
According to studies, systematic exercise:
1.reduces the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases and diabetes mellitus as well as hypotensive episodes after dialysis session
2.contributes to better regulation of blood pressure
3.reduces the symptoms of depression and anxiety
4.improves the quality of sleep and thus the quality of life
5.contributes to better control of body weight and to the improvement or maintenance of muscle mass
7.reduces the symptoms of fatigue and general exhaustion
8.improves dialysis markers and reduces potassium levels when done during dialysis sessions
What are the basic safety rules for exercise programs to be effective?
The participation of patients with CKD in exercise programs is contraindicated in cases such as unregulated hypertension, severe cardiac arrhythmias, unstable angina, active liver disease, unregulated diabetes mellitus, severe cerebral and peripheral vascular disease, persistent hyperkalemia prior to dialysis as well as a serious orthopedic problem; or even if the patient has experienced a recent acute myocardial infarction. In general, patients with CKD, although they may suffer from other illnesses, they are not excluded from participating in the exercise programs since it has been noticed that systematic exercise has a positive effect on reducing the severity of concomitant diseases.
What kind of exercise is appropriate for my condition?
In patients with chronic renal disease the following are recommended:
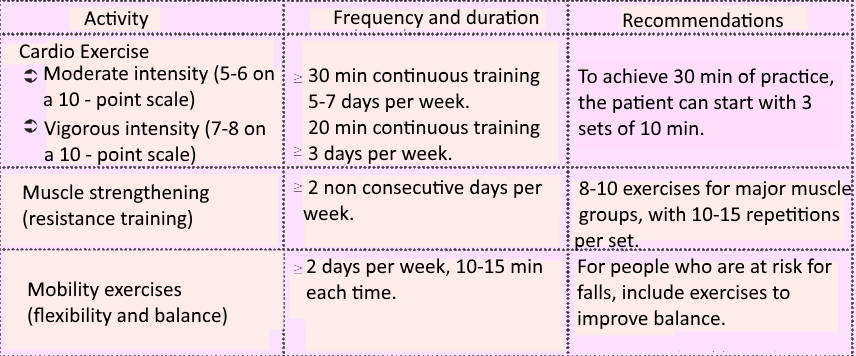
(a) aerobic exercise of low to moderate intensity (5 - 7 times a week) for at least 30 minutes / day. For dialysis, the best form of exercise is cycling during session (30 - 45 minutes), while for peritoneal walking is mostly recommended (between changes).
b) exercises with resistance or body weight (2 to 3 times a week).
In general:
-Exercise wisely.
-Avoid outdoor exercise when the ambient temperature is too high or too low.
-Do not exercise when:
a) you have a fever (body temperature above 38.3 ° C), b) you have missed a dialysis session, c) you have a disease that has not yet been treated, or d) your exercise is causing pain.
Recommendations for physical activity in the elderly or younger people with a chronic illness and / or some physical limitation
By the Scientific Director Aristides Paraskevopoulos
Bibliography
1.G. Kosmadakis, J. Boletis, Physical exercise in patients with chronic kidney disease. Dialysis Unit «Pantokrator», Clinic, Athens, Department of Nephrology and Transplantation Unit, General Hospital «Laiko», Athens, Greece. Hellenic Nephrology 2011; 23 (1): 28-36.
2.I. Katschitis, The effect of an exercise program to stress during dialysis session", Postgraduate dissertation, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki - Department of Physical Education and Sports Science, Interdepartmental Postgraduate Program of Studies. Thessaloniki, 2015
3.S. Vrakas, The effect of an exercise program accompanied by music on patient’s anxiety with CKD undergoing dialysis. Postgraduate dissertation. Aristotle University of Thessaloniki - Department of Physical Education and Sport Science Postgraduate Program of Studies "Physical Activity and Quality of Life", 2016.
G. Vasilios, K. Karatrantou, V. Manou, V. Paschalis, S. Kelli, Exercise as a means of prevention and rehabilitation of chronic diseases, Trikala, 2013.
4.M.E. Nelson, W.J. Rejeski, S.N. Blair, P.W. Duncan, J.O. Judge, A.C. King, C.A. Macera, C. Castaneda-Sceppa, Circulation 116 (2007) 1094-1105.
